AMR
Autonomous Mobile Robots
The integration of AMR systems, or Autonomous Mobile Robots, offers numerous advantages for your robotic cell and production line.
ECM Robotics supports you throughout your integration project.

Robotics integration expert
Automate your factory with Autonomous Mobile Robots
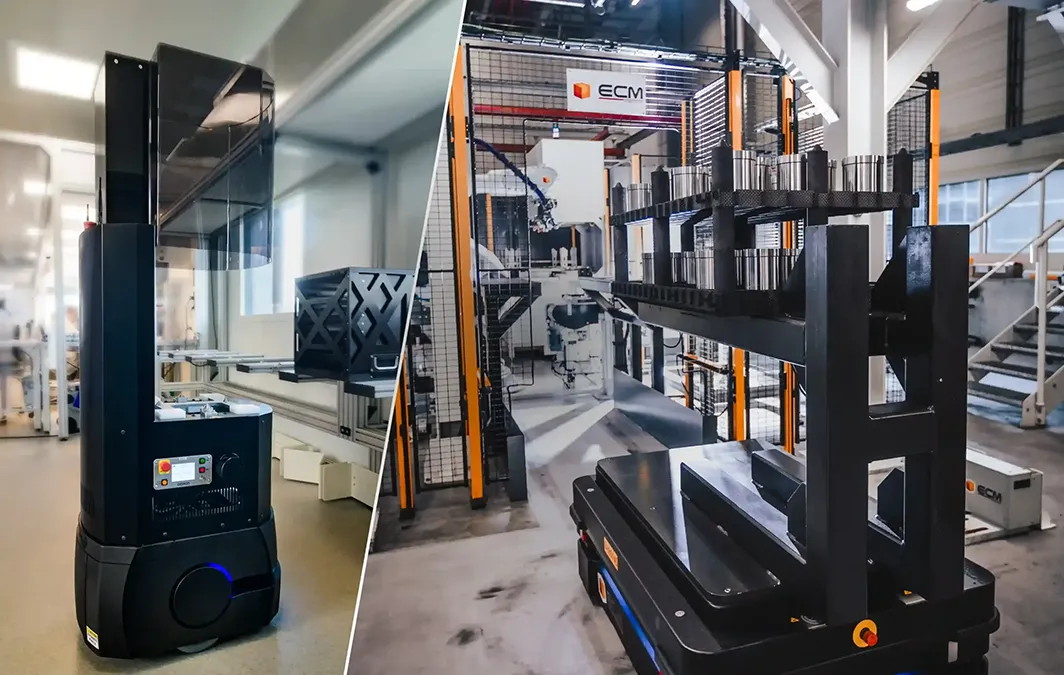
Thanks to its extensive expertise in integrating robotic solutions, ECM Robotics is able to offer AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robot) systems adapted to a wide variety of environments, ranging from industrial settings to cleanroom facilities. Whether it’s handling heavy loads or fragile components that require high precision movement, our experts provide you with customized solutions and support you at every stage of the integration project.
How do autonomous
mobile robots fit in.
An AMR is an autonomous mobile robot capable of moving freely in an environment without a predefined path. Using sensors, cameras, lidars, and advanced navigation algorithms, the AMR maps its environment in real time and adapts its path according to obstacles and changes in context.
Autonomous mobile robots are integrated into factories to automate the transport of loads between different areas without requiring fixed infrastructure (rails or magnetic strips). This system coexists easily with operators and other equipment and adapts well to changes in the site.
AMR :
direct benefits for your production.
The integration of an AMR system in a factory offers unmatched flexibility and efficiency in industrial environments.
Overcoming infrastructure constraints
These autonomous mobile robots allow you to easily move robotic cells around the workshop without being constrained by fixed infrastructure.
No more need for traditional conveyors
By eliminating the need for traditional conveyors, they reduce installation complexity and free up valuable floor space.
Reduction in manual handling
They also minimize manual handling operations, thereby improving ergonomics and productivity.
A system that coexists with the rest of the workshop
AMR systems work with people and machines without major disruption.
SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) technology is a method used by autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to navigate autonomously in an unknown environment. It allows the robot to build a map of its environment while locating itself on that map in real time. SLAM works by using onboard sensors such as lidars, cameras, IMUs (inertial measurement units), and sometimes ultrasonic sensors. By cross-referencing the data from these sensors, the robot can :
- map the environment (identify walls, obstacles, passageways)
- determine your position and orientation in this space, even without GPS
- correct your location errors by adjusting the map with each new observation
- navigate safely and efficiently, avoiding obstacles and planning optimized routes.
There are several variants of SLAM, including Visual SLAM (V-SLAM), which primarily uses cameras. The choice of method depends on the constraints of the environment and the onboard hardware. Thanks to SLAM, AMRs can operate in dynamic and unstructured environments without requiring fixed infrastructure or pre-established maps (unlike AGV technology—automated guided vehicles), which improves their flexibility and autonomy.
Use cases for
AMR.
AMRs are revolutionizing many industries thanks to their ability to move and operate autonomously in dynamic environments. Here are three key areas where their use is particularly strategic.

Internal transport
of goods.
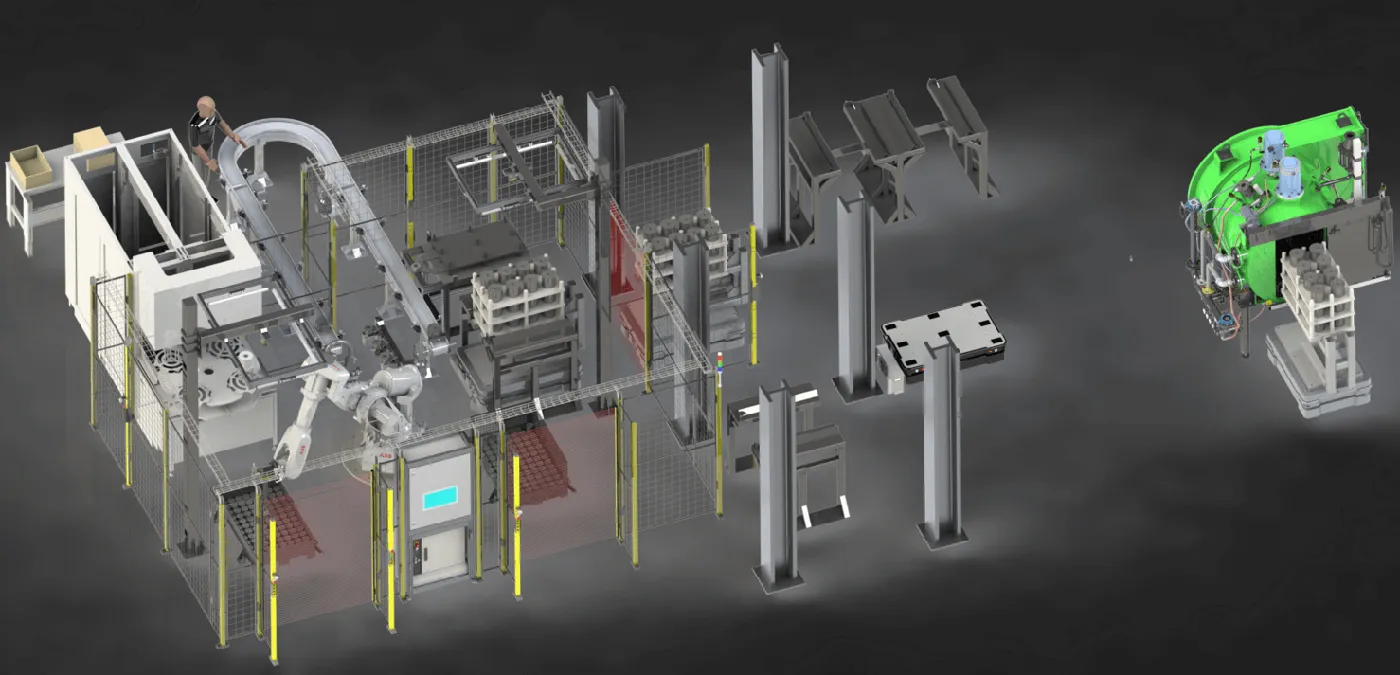
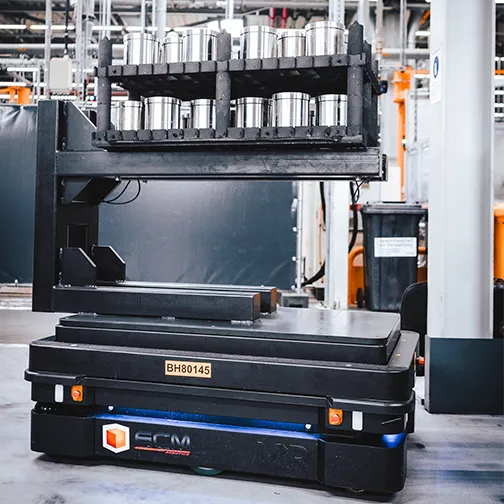
In factories, AMRs are widely used for the autonomous transport of materials, parts, or finished products.
- Transfer of bins or pallets between storage areas and production lines.
- Automatic delivery of consumables.
- Restocking of workstations without human intervention.
Advantage: reduction in manual transport time, freeing operators for higher value-added tasks.

Automated systems embedded
in AMRs.
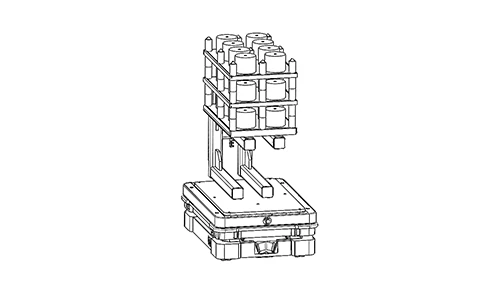
AMRs can be equipped with onboard automated modules that enable them not only to transport loads, but also to actively interact with their environment or automate specific tasks. This transforms them into intelligent and versatile mobile units.
- Motorized conveyors : for automatically loading or unloading bins or cartons onto fixed stations or dynamic racks, without human intervention.
- Linear axes or lifts : for adjusting the height at which objects are deposited or picked up, enabling integration with machines or shelves at different levels.
- Cameras and industrial vision systems : for quality control, barcode reading, or locating a specific point on a workstation.
- RFID or 2D code readers : to track goods, validate logistics operations, or trigger automated actions depending on the object being transported.
Advantage: these modules significantly increase the capabilities of AMRs, which no longer simply “move” loads, but can interact autonomously and intelligently with their environment, contributing to more refined and scalable automation.

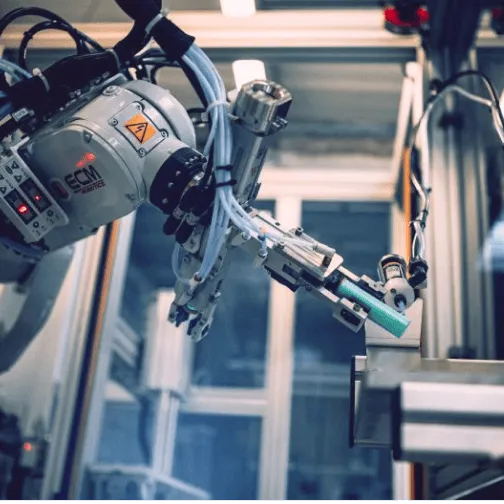
Onboard robots.
Some AMRs are mobile platforms on which other robotic modules are mounted, forming hybrid systems.
- Robotic arm mounted on an AMR to perform mobile picking or assembly tasks.
- 3D scanner or on-board camera for inspection or quality control missions.
Advantage: mobility combined with manipulation or perception capabilities, expanding use cases to complex and dynamic tasks.
Do you have a project ?
Would you like more information, to entrust us with a project, or to meet our professionals ?
Fill out our form and our teams will get back to you as soon as possible !